Describe the Organization of Egyptian Society
The pharaoh was the head of state and the divine representative of the gods on earth. The first and most liberal of these was the 1923 constitution which was promulgated just after Britain declared Egypts independence.

Egyptian Social Structure Ushistory Org
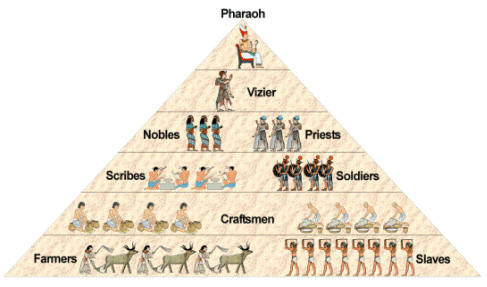
The ancient Egyptian social hierarchy placed the Pharaoh at the top and the farmers and slaves at the bottom.

. Ancient Egypt was an ordered society with a distinct hierarchy. All the pharaohs of the same family formed a. Political organization of Egyptian civilization Egyptian society was made up of a descending hierarchy of the gods the king the blessed dead and humanity the people.
Egyptian Social Hierarchy. During the early stages of Mongol supremacy the empire established by Genghis absorbed civilizations in which a strong unified and well-organized state power had developed. Egypt has operated under several constitutions both as a monarchy and after 1952 as a republic.
Religion and government brought order to society through the construction of temples the creation of laws taxation the organization of labour trade with neighbours and the defence of the countrys interests. Many monuments contain much detailed information about ancient Egypt including their scientific knowledge that gave them the ability to build such structures. Map of Ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean and Red seas.
Three classes of Egyptian society. Terms in this set 38 Mathematics. Peasants were the fifth tier of society with slaves making up the lowest social class.
Even before the Old Kingdom period the foundations of Egyptian civilization were being laid for thousands of years as people living near the Nile increasingly focused on sedentary agriculture which led to urbanization and specialized non-agricultural economic activity. The powerful officers formed a structure and were responsible for fulfilling the political duties. Egyptians believed that the gods controlled the universe.
Its structure began to emerge in the Old Dynasty with upper and lower classes of people. First was the class of people below the pharaoh. The nuclear family was the core of Egyptian society and many of the gods were even arranged into such groupings.
Jeff has taught US and World History at the high school and college levels for nearly ten years and has a masters degree in history. There was tremendous pride in ones family and lineage was traced through both the mothers and fathers lines. Below the pharaohs came high priests and priestesses and government officials and then the small class of artisans scribes and.
In order for Egyptologists to help fill in the gaps of social structure in Ancient Egypt much research would continue to be conducted. However the political structure even then was divided into different levels and responsibilities were divided according to a hierarchical structure. Egyptian society was structured like a pyramid.
Egyptians can do simple math add and subt Astronomy. The social structure of ancient Egypt can be sorted into a social pyramid. The pharaoh was assisted by a hierarchy of advisors priests officials and.
During the ancient Egyptian days the country was run different from how it is run today. The middle class was made up chiefly of merchants manufacturers and artisans. They believed that the god controlled their lives and they.
The government was under the command of the king or pharaoh who for the ancient Egyptians was a divine being who acted as a link between humans and the gods and was the protector of the. As this great kingdom developed a middle class of craftsmen emerged. In addition pharaohs were considered gods.
The demands of an expanding empire offered opportunities for. The third tier consisted of the scribes and soldiers with the middle class in the fourth level. The pharaoh stood at the center of Egyptian religion as well as its government and army so the pharaoh controlled all aspects of Egyptian life.
Good at it bc Egyptians can see the night sky very well. Antagonism existed between a society of this nature and the. We can call it the upper class.
The social organization of the Mongols was however characterized by pastoralism and a decentralized patrilineal system of clans. They were not elected they inherited the kingdom from their ancestors. 1 Ancient Egypt had a highly organized society.
Social Structure Political Organization. Decimal based on power of 10. The Pharaohs were the community of people who were the richest and the most powerful.
Beginning with the Old Kingdom the Egyptians created a complex but efficient administrative system that supported the absolute authority of the pharaoh. The government stored food and distributed it to workers or to the people in times of famine. People paid taxes with agriculture produce or precious materials.
Broadly speaking the Egyptian society manifested God at the top position. At the top were the gods such as Ra Osiris and Isis. At the top of the social pyramid was the pharaoh with the government officials nobles and priests below himher.
Egyptian kings were called pharaohs. That document laid the political and cultural groundwork for modern Egypt declaring it an independent sovereign. The upper class consisted of the royal family rich landowners government officials important priests and army officers and doctors.
The lower class the largest class by far consisted of unskilled labourers. Ancient Egypt had three main social classes--upper middle and lower. Egypt was divided into nomes and a nomarch governed each one.
They could make the Nile overflow cause famine or even bring death. Yet things were beginning to change. Therefore it was important to keep them happy.
Temples were built to honor their gods. There were three classes in the ancient Egyptian society. Describe the organization of Egyptian society.
Ancient Egyptian Political Hierarchy.
Egyptian Social Classes And Society History

Ancient Egypt S Social Structure Ck 12 Foundation

Ancient Egyptian Hierarchy Facts Ancient Egypt Projects Ancient Kush Hierarchy
No comments for "Describe the Organization of Egyptian Society"
Post a Comment